The Rate of Reactions in Chemical Kinetics easy To Understand
When we listen to the term Rate what we thought normally absolutely we thought about the speed of something but in Chemistry concept many reactions take place and those have some Rate(speed) to complete the process there are three types of Rate Of Reactions like fast reaction, moderate reaction, and slow reaction.
The Rate of Reaction definition
"The quantity of a reactant species consumed or the quantity of a product species formed in unit time in a chemical reaction is called the rate of reaction"
There are three types of reactions
- Fast Reactions or Instantaneous Reactions
- Moderate Reactions
- Slow Reactions
Fast Reactions
These reactions are completed immediately. These reactions are mostly ionic in nature. It is difficult to determine the Rate of these reactions.
The reactions which are taken a very short time period for completion is called the fast reaction. Here Rate of Reaction cannot be measured accurately.
Ex-
The reactions which are taken a very short time period for completion is called the fast reaction. Here Rate of Reaction cannot be measured accurately.
Ex-
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (solid)
Moderate Reactions
These Reactions are completed in a measurable time period. These are mostly molecular reactions.
The Reactions which takes measurable time period for completion is called Moderate Reaction. There are Rates of reaction can be measured accurately.
Ex-
The Reactions which takes measurable time period for completion is called Moderate Reaction. There are Rates of reaction can be measured accurately.
Ex-
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH
Slow Reactions
These Reactions Consume much time to be completed.
The Reaction which takes a very long time period for completion is called the slow reaction.
Ex-
Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, Oxidation of copper in the presence of moisture to form basic copper carbonate, Rusting of iron in the presence of moisture.
The Reaction which takes a very long time period for completion is called the slow reaction.
Ex-
Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, Oxidation of copper in the presence of moisture to form basic copper carbonate, Rusting of iron in the presence of moisture.
Fe + H2O + CO2 → Fe(OH)(HCO3)
Average Rate Of Reactions
Also, we can determine the average rate of reaction as follows
It is defined as the rate of chemical reaction change of Concentration per unit time
= Change of concentration in given time Per Total Time Taken = Δx/Δt
Instantaneous Rate
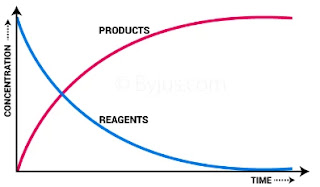
In case of a reaction, the average rate has no meaning since the rate of reaction is always changing with time. As it is well known from the law of mass action that the rate of a reaction at any instance is directly proportional to the concentration or active mass of the reactants at that time. This rate is called Instantaneous rate and can be defined as the rate of change of concentration of any one of the reactants or products at a specific instant of time.
If during an infinitesimally (very very short) small interval of time, During which rate must have remained constant and dx should be a very small change in concentration, then,
[ Instantaneous rate of reaction = Δx/Δt =LtΔt→0 × Δx/Δt ]
Some Factor affecting the rate of reaction
The concentration of the reaction:
We know that the molar concentration of the reactants is maximum to start with and thus, the rate of reactions is also maximum in the beginning. As the reaction proceeds, the molar concentration of reactant goes on decreasing and hence the rate also decreases. Clearly, the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the molar concentration of the reactant for example if a candle is lighted in a cylinder, the glow of light diminishes as the oxygen in the cylinder is consumed.
Nature of the reactant:
The rate of reaction varies from one reaction to the other even if the concentration and temperature are kept the same
The reason for this is that reactant with weak bonds react quickly. Also, the reactant having strong chemical bonds break with difficulty and hence reaction rate is slow.
Temperature:
The rate of reaction greatly depends upon temperature. It has been found that the rate of reaction is almost doubled by an increase of just 100 C, experimentally it has been found that for each 100 C rise in temperature, the rate of decomposition of H2O2 increase by some factor.
Catalyst:
A catalyst is defined as a substance whose presence increases the rate of the chemical reaction. The catalyst does not itself undergo any change in the chemical composition at the end of the reaction.
Radiation:
The rate certain reactions are considerably increased in pressure of radiations. The photons of these radiations process sufficient energies to break bonds in the reactant species. We know that H2 and Cl2 react very slowly in the absence of light but take place rapidly in presence of light.
H 2 + Cl2 ž 2HCl
Such reactions are called photochemical reactions.
Surface area:
In heterogeneous reactions, the surface area of reactant plays an important role. With the increase in surface area or with the decrease in the particle size of reactants, the rate of reaction increases. The reason is that for the same mass of the substance, a larger surface is provided for the reaction. For example (i) coal dust burns brilliantly than a lump of coal (ii) wood chips burn rapidly than a log of wood.
Characteristics of the rate constant:
(1)Different reactions have different values of the rate constant at a given temperature.
(2)The higher value of K faster is the unity.
(3)The value of K at a given temperature is most characteristic of the reaction.
(4)For a reaction, the value of rate constant (K) changes with temperature.
(5)The unit of the rate constant depends upon the order of reaction.


0 Comments