Activation Energy
The reactant molecules in a
chemical system have initial energy of their own. It is essential for them to
acquire threshold energy before they react chemically. The extra energy
supplied to the reactant molecules to attain threshold energy to undergo
chemical reaction is called activation energy.
Activation
energy (Ea)=(Threshold energy)-(average K.E. of reacting molecules)
“Activation
energy is defined as the excess energy which must be supplied to the reactant
molecules in the ground state so that they may acquire the desired threshold
energy , collide effectively, form the activated complex and hence the
products.”
For fast
reactions-activation energy is low.
For slow
reactions-activation energy is high.
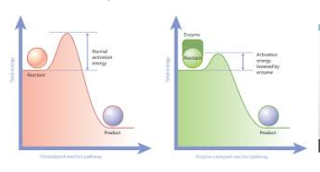
Activation
energy of a chemical reaction can be illustrated in an energy level diagram.
The hump between the reactants and the products is called the energy barrier.
It is possible only when the reactant molecules possess energy equal to
threshold energy.
Activated
Complex
It is the
highest energy state of a reaction and is most unstable.
Activated
complex formed at once gets converted into product molecules. When the reactant
molecules having threshold energy collide with one another, an activated
complex is formed.
During the
formation of this complex, the bonds in reactant molecules start breaking and
bonds in the product molecules start formation. The activated complex is also
called the transition state. Consider the reaction between H2 and I2. When
requisite amount of energy is supplied, the reactant molecules undergo a change
forming activated complex.
Applications of Activation energy
1.
For
some reactions, the activation energy may be very high and for others, may be
very low. This determines the conditions for the reaction to take place.
2.
Depending
upon the value of activation energy, the fraction of the total number
collisions which are fruitful may be very small, moderate or high.
3.
Activation
energy for explosive mixture as that of
(i)
Methane
+ oxygen
(ii)
Hydrogen
+ oxygen etc. Is very high. Hence, they do not react at ordinary temperature.
However, the initiation of such reactions take place with explosion on account
of release of tremendous energy, which is distributed among other molecules and
the fraction increases.
Visit www.topposts.in for more and latest news

0 Comments